Imagine a single food, affordable and versatile, that provides almost every nutrient your body needs. That food isn’t a trendy supplement or an exotic berry—it’s the humble egg.
Once unfairly vilified for its cholesterol content, modern nutritional science has fully vindicated the egg. It’s now celebrated as one of the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet. This post is your definitive guide to understanding why the egg is a nutritional marvel, breaking down its powerful profile of protein, vitamins, and health benefits.
The Macronutrient Breakdown: Calories, Protein & Good Fats
Let’s start with the basics: what you get from one standard large egg (approx. 50g).
A. Calorie Count: A Low-Calorie Powerhouse
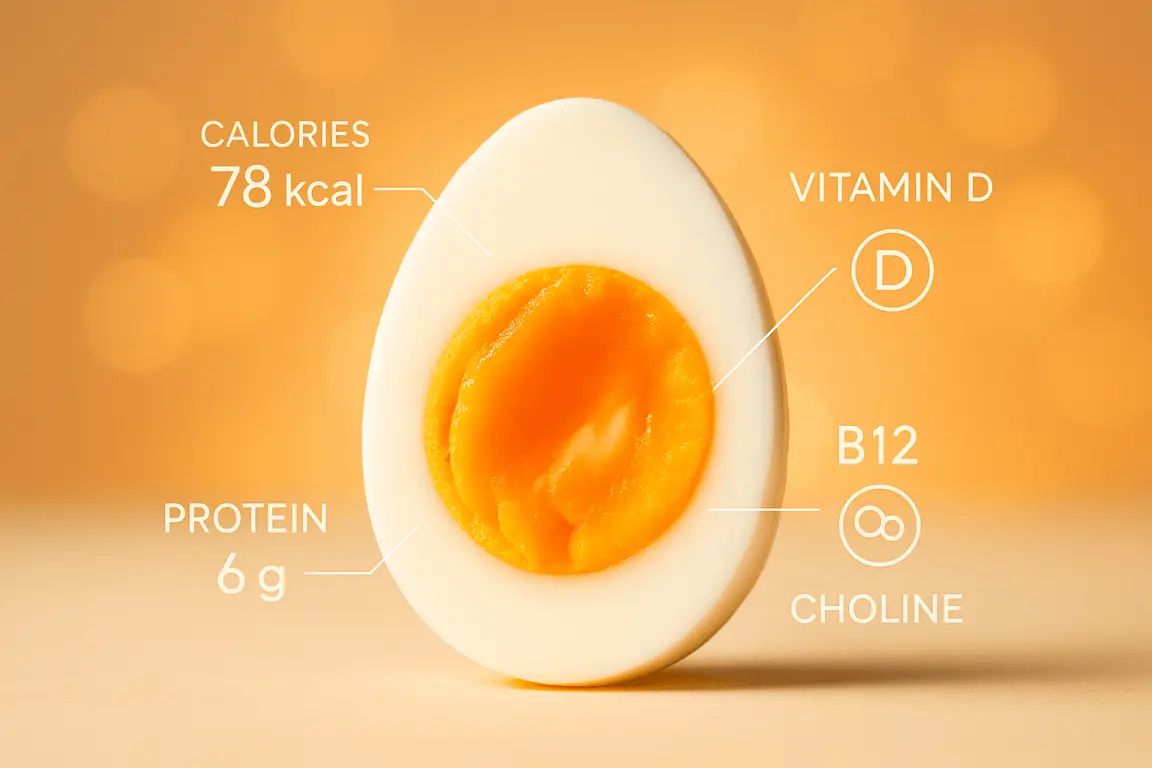
One large boiled egg contains approximately 70-80 calories. This makes it an incredibly efficient source of energy and nutrition. The calories are split between:
- The Yolk: Contains most of the calories from healthy fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
- The White: Provides a significant portion of the calories from pure protein.
B. The Complete Protein Source
Eggs are the gold standard for protein quality.
- Quantity: One large egg delivers about 6-7 grams of high-quality protein.
- Quality: Egg protein is a “complete protein”—it contains all 9 essential amino acids in the right ratios that our bodies cannot produce on their own. This makes it exceptional for muscle repair, tissue growth, and promoting satiety (the feeling of fullness), which aids in weight management.
C. Healthy Fats & The Cholesterol Myth
- Fat Content: An egg contains about 5 grams of fat. The majority of this is healthy unsaturated fat, with only a small portion being saturated.
- The Cholesterol Clarity: The yolk contains roughly 185 mg of dietary cholesterol. For decades, this caused concern. However, extensive research now shows that for most healthy people, dietary cholesterol from eggs has a minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels. The body’s own production of cholesterol is influenced more by saturated and trans fats. For the majority, eggs can be part of a heart-healthy diet.
The Vitamin & Mineral Treasure Trove
An egg is far more than just protein and fat; it’s a concentrated source of essential micronutrients.
A. Essential Vitamins
- Vitamin D: One of the few natural food sources of Vitamin D, crucial for bone health, immunity, and mood regulation.
- Vitamin B12 & B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Vital for energy production, red blood cell formation, and nerve function.
- Vitamin A: Supports vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Choline – The Brain Booster: Eggs are one of the best dietary sources of choline. This critical nutrient is essential for brain development, memory function, and liver health. It’s especially important for pregnant women for fetal brain development.
B. Key Minerals
- Iron: Carries oxygen in the blood. While the iron in eggs (non-heme iron) is less readily absorbed than that in meat, it still contributes to daily needs.
- Selenium: A powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage and supports thyroid function.
- Phosphorus & Zinc: Support bone health and immune function.
Yolk vs. White: Where Does the Nutrition Lie?
It’s time to end the debate and give the yolk the credit it deserves.
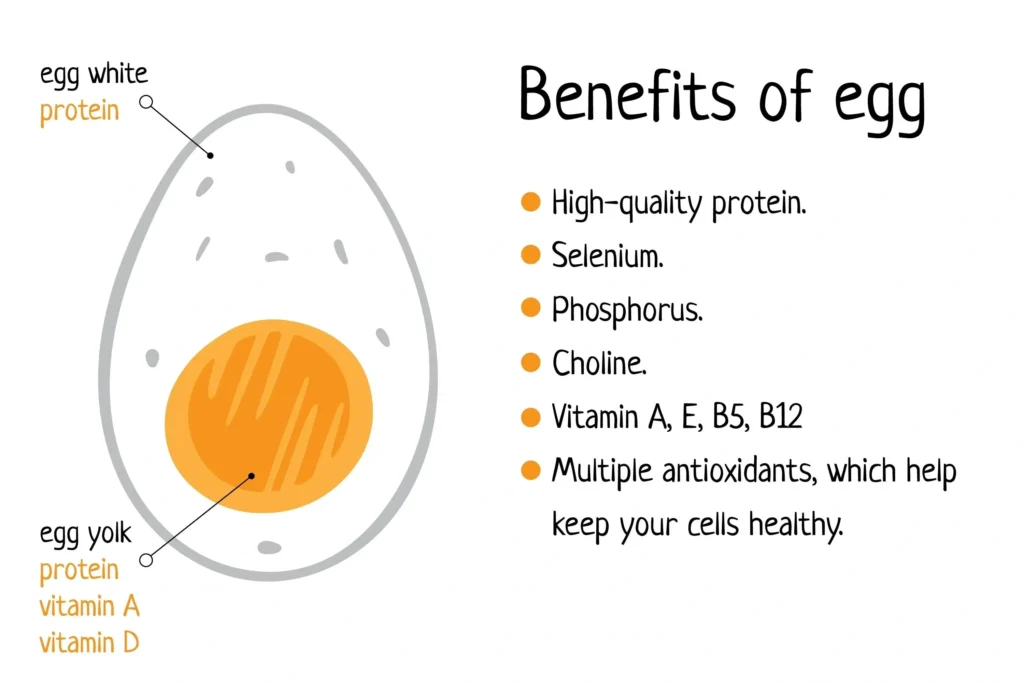
The Egg White (Albumen):
- Primarily protein (about 3.6g) and water.
- Contains virtually no fat or cholesterol.
- Has minimal vitamins and minerals compared to the yolk.
The Egg Yolk:
- Contains almost all the vitamins and minerals: Vitamins A, D, E, K, B12, Choline, and the antioxidants Lutein and Zeaxanthin.
- Holds all the healthy fats.
- Is the source of dietary cholesterol and about half of the egg’s protein.
The Verdict: Unless you have a specific medical condition advised by a doctor, eat the whole egg. Discarding the yolk means you’re throwing away the most nutrient-rich part.
Top Health Benefits of Including Eggs in Your Diet
- Superior Eye Health: Rich in the antioxidants Lutein and Zeaxanthin, which accumulate in the retina and help filter harmful blue light. They significantly reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
- Effective Weight Management: The high-quality protein in eggs increases satiety, reduces hunger hormones, and helps you feel full longer. This can lead to a natural reduction in calorie intake throughout the day.
- Supports Brain Health & Development: The choline in eggs is a key building block for neurotransmitters. Adequate choline intake is linked to improved memory, cognition, and is vital during pregnancy and infancy.
- Promotes Heart Health: For most people, regular egg consumption can help modify the pattern of LDL (“bad”) cholesterol particles to a less harmful subtype, while raising HDL (“good”) cholesterol, contributing to a better overall lipid profile.
Conclusion: The Indisputable Superfood
The egg is a near-perfect nutritional package: a complete protein, loaded with brain-boosting choline, eye-protecting antioxidants, and essential Vitamin D—all for under 80 calories. It’s a gift from nature that supports fitness goals, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
Ready to make eggs a staple of your healthy diet? Before you add them to your cart, ensure you get the best value. Check the live, daily updated egg prices in your city on TodayEggRate.com to source this powerhouse superfood at the most affordable rate.